RisaSimon
RisaSimon
Living Kidney Donors Day 2018
The State of Arizona recognizes Living Kidney Donors as life-saving humanitarians who inspire our community to “give back” in bigger and bolder ways in Arizona’s HCR 2042 proclamation resolution for Living Kidney Donors Days in 2018.
Over 100,000 end-stage kidney disease patients nationwide pray their name will make it to the top of the list, so they can get a life-saving kidney transplant. The average wait for a deceased donor’s kidney is four and a half years; in some regions, the wait can be as long as nine years. Yet, there is a way to end this wait and improve outcomes, if communities were better informed.
Arizona State Representative Heather Carter teamed with TransplantFirst Academy founder, Risa Simon on March 8, 2018, to re-introduce resolution proclamation, HCR 2042, to make March 8, 2018 Living Kidney Donors Day in the state of Arizona. This renewal initiative is intended to extend statewide awareness and recognition in living kidney donation.
By design, the proclamation falls on World Kidney Day and Donor Network of Arizona’s Donate Life Day, to further expand collaborative efforts to expand awareness. Simon said, “Since living kidney donors don’t wear a Medal of Honor or a superhero’s cape, it’s often hard to recognize them. They deserve a lifetime achievement award for the role they play in saving lives and inspiring community citizens to give back in bigger and bolder ways.”
The significance behind HCR 2042 is that it represents hope for nearly 2,000 people in Arizona who are in desperate need of a kidney transplant. The names of these individuals reside on a list with a 3 to 5 year waiting period. Sadly, 90 names are removed from that list each year when patients die while waiting for their much-needed transplant. Another 50 Arizonans are removed from the list due to advanced illness, which often disqualifies them from ever receiving a transplant.
The good news is that each year approximately 575 people in Arizona are removed from the list because they received a kidney transplant. The bad news is that the list and its wait never gets any shorter. This quagmire exists because an additional 865 new names are added every year (290 more than those removed). This impossible balancing act and its life-threatening challenge continue to disrupt organ donation supply and demand.
Living kidney donation, however, holds the potential to course-correct the destiny of this deadly foregone conundrum. Simon asserts, “Our organ shortage stems from a lack of education and awareness.” She describes the statewide proclamation as a befitting salute that increases awareness and right-doing. She went on to say, “the noble acts of living kidney donors don’t end after donation. Their gift represents more than one-life saved. Their actions live on to inspire ordinary people to seek extraordinary ways in which they can engage in life-saving opportunities for others in need.”
As a recipient of a live-donor kidney transplant, Simon said, “While those of us who were blessed with a transplant from a living donor will be forever grateful, we must not forget those left behind. Living kidney donors embody the promise of a better life and a better tomorrow. Now we need to make it a better life and a better tomorrow for all.”
One of those humanitarians is Kati Walker, a living kidney donor who donated one of her kidneys to her children’s elementary school principal in Cave Creek, Arizona. Kati has since become a strong advocate for living kidney donation and an inspirational spokesperson for the TransplantFirst Academy. Post-donation, Kati’s active life remains full of love and joy. Even after her donation, she continues to give back at every turn. There’s no prompting needed when you hear Kati affirm her kidney donation was “one of the best decisions I ever made!”
To date, more than 145,000 living kidney donors have selflessly saved an equal number of lives, over 2,800 of whom were saved in Arizona. We salute them all and are hopeful more good-hearted Samaritans will follow Kati’s lead. Last year, living kidney donor transplants dropped down 39% from 2009 in Arizona alone. Through increased awareness, the TransplantFirst Academy and other organizations, like the National Kidney Foundation of Arizona and the Erma Bombeck Project, believe Living Kidney Donor’s Day holds great promise by shining light on increased awareness and recognition that can lead to a better and longer life for all.
About TransplantFirst
TransplantFirst Academy is a 501c3 non-profit organization based in Phoenix, dedicated to empowering kidney patient outcomes and increasing living kidney donor awareness. For more information, visit: TransplantFirst.org. To request an interview, contact TransplantFirst’s founder/CEO, Risa Simon, at (480) 575-9353 or via email at risa@transplantfirst.org
# # #
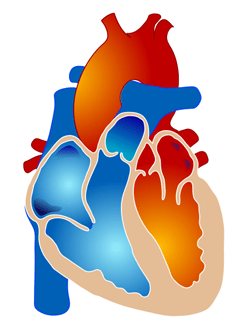
Cardiac Benefits Following Kidney Transplant
A recent study from Kidney and Blood Pressure Research describes increased heart health in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients after receiving a kidney transplant. A common side effect of CKD is high blood pressure and left ventricular hypertrophy, which occurs when the heart’s main chamber (responsible for releases blood and oxygen to the rest of the body) becomes thicker and less effective.
While our heart and kidneys play an important and most supportive role to one another, they function very differently. For starters, the heart pumps blood through the body, and our kidneys take waste out of the blood.
Every day, our kidneys filter about 120 to 150 quarts of blood to produce about 1 to 2 quarts of urine, composed of wastes and extra fluid. The heart, on the other hand, has chambers and values that control how arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart.
As the chambers become less effective they cause strain on the heart that can force the left ventricle to work harder. As the workload increases, the muscle tissue in the chamber wall thickens. When the heart muscle becomes enlarged, it can lose elasticity and eventually become too weak to pump with adequate force. This weakness can result in a variety of risk factors ranging from cardiac fatigue to complete heart failure.
While we are well aware of the supportive connection between cardiac function and renal function, we now know more about the benefits of how a good functioning kidney can support heart health.
In one study,(3) researchers obtained blood samples, electrocardiograms, ultrasounds of left heart chambers, and Doppler recording showing blood flow from thirty-one CKD patients before and after their transplant. The conclusion demonstrated that transplant patients had a decreased consequence of the negative cardiac effects after their kidney transplant.
It is believed that transplanted patients are better able to lower systolic blood pressure and in turn, decrease the thickness of the left ventricle structure.
References:
- https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/howtheheartworks.html
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/kidney-disease/kidneys-how-they-work
- Hewing, Bernd, et al. “Improved Left Ventricular Structure and Function After Successful Kidney Transplantation.” Kidney and Blood Pressure Research, vol. 41, no. 5, 10 Oct. 2016, pp. 701–709., doi:10.1159/000450559.
- Özkaya, Özge. “Kidney Transplants Seen to Improve Aspects of Cardiac Health in CKD Patients.” CKD News, BioNews Services, 26 Oct. 2016
For more information about how to end your wait for a kidney transplant or find potential living kidney donors, visit https://transplantfirst.org or check out this patient empowerment book by Risa Simon: In Pursuit of a Better Life .
AST Releases Live Donor Toolkits
Are you (or someone you know) contemplating the possibility of becoming a living kidney donor? If so, the American Society for Transplantation (AST) just made your discovery process a lot easier. This just released, the first-ever, Live Donor Toolkit for individuals who want to learn more about living organ donation. From cost worksheets to medical implications, you’ll find it all and more in this comprehensive guide.

This one of a kind toolkit was created to help interested individuals navigate complex questions surrounding financial and medical considerations involved in living kidney donation.
While a reassuring 97.5% of live organ donors say they would donate again if they could, it’s important to learn as much as you can about living donation before considering this extraordinary gift of life.
There are potential medical, psychosocial, and financial impacts associated with donating an organ. That said, interested donors need access to that information, and the best way to provide it would be in a centralized educational format. This toolkit does that and more.
AST’s educational toolkit was created specifically to improve the availability and delivery of quality education for those considering live donation. It was also created to expand living donation messaging to reach those who might consider live donation if they knew more about it. Additionally, this toolkit offers educational content that can be used across the transplant community.
Described as being housed under two umbrellas, the Live Donor Financial Toolkit and the Live Donor Medical Impact Toolkit offer 10-15 stand-alone chapters each. As an added bonus, the Medical Impact Toolkit includes chapters written for both provider-level and patient-level comprehension.
Here’s a sample list of chapters in the Medical Impact Toolkit:
- Hypertension in the Living Donor
- The Obese Kidney Donor
- The Living Donor Who is at Risk for PKD
- Donor Surgery – Post-op Complications
- What is the ESRD Risk for Living Donors
- Psychosocial Risks of Living Kidney Donation
- Pregnancy Outcomes after Live Kidney Donation
- Living Donation in Paired Exchange
Here’s a sample list of chapters in the Financial Toolkit:
- Lost wages due to recovery time
- Missing work from the evaluation
- Using up vacation, holiday, and sick days
- Concerns that the employer might not support a person’s absence from work
- Transportation for testing, surgery and follow up care
- Travel, meals and lodging expenses (out of town donors)
- Related caregiver, child care, elder care, pet care costs during recovery
Click on the toolkit image below to learn more:

For more information on how to share your story, increase need awareness and potentially meet individuals who might be interested in learning more about living kidney donation and/or becoming a living kidney donor for someone in need, visit: www.findingkidneydonors.com
Stem Cells Replacing Immunosuppressants?
 Imagine the day when a transplant recipient could consider stem cell treatment instead of taking a lifetime of immunosuppressants to prevent rejection. Of course, the threat of organ rejection is a serious concern for those who receive a kidney transplant, and immunosuppression is needed to prevent the transplant recipient’s immune system from recognizing the donated kidney as a foreign object, with different DNA. Yet, immunosuppressants are not without risk.
Imagine the day when a transplant recipient could consider stem cell treatment instead of taking a lifetime of immunosuppressants to prevent rejection. Of course, the threat of organ rejection is a serious concern for those who receive a kidney transplant, and immunosuppression is needed to prevent the transplant recipient’s immune system from recognizing the donated kidney as a foreign object, with different DNA. Yet, immunosuppressants are not without risk.
While immunosuppressants are designed to prevent the patient’s immune system from attacking the donor kidney, they can also present problems. Those problems include an increased risk for nephrotoxicity, an inability to fight off pathogens, and the increased risk for diabetes, heart disease, and even cancer.
Another issue surrounding immunosuppressants is tied to the cost of the medication. Immunosuppressant medications can cost up to $14,000 every year for the rest of a kidney recipient’s life, depending on insurance coverage. Despite these negative aspects, immunosuppressants have the most common and most effective way to prevent rejection in organ transplant recipients.
Earlier this year, California’s Stem Cell Agency (CIRM) approved funding for further research and clinical trials by involving the use of stem cells to prevent organ rejection from a donor. The hope for this new research is to discover alternatives to immunosuppressants medications.
One of those alternatives is known as stem cell treatments. Stem cell treatments involve collecting stem cells from the donor’s bone marrow with the goal of introducing them into the directed kidney transplant recipient before the transplant is performed.  Stem cell treatments allow the patient’s immune system to recognize the donor’s cells and begin to adapt prior to receiving the donor kidney.
Stem cell treatments allow the patient’s immune system to recognize the donor’s cells and begin to adapt prior to receiving the donor kidney.
Advancements in stem cell research are shinning a hopeful beam of light on the reduced risk of rejection, fewer side effects, adverse events and costs for immunosuppressants.
Risa Simon, Founder/TransplantFirst Academy / www.TransplantFirst.org
Proactive Engagement Improves Outcomes for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Approximately 30 million American adults have Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), yet only 10% are aware they have it; the other 90% have no clue. Patients find themselves completely baffled when they are told they’ve lost significant kidney function without prior warning. For those who crash into renal failure, their confusion turns to outrage once they realize that an opportunity to change their fate no longer exists.
How can this life-threatening disease be missed by our healthcare system’s radar and cause such a negative impact to so many lives? The answer to that question continues to challenge most patients and providers. Aside from the fact that CKD has no recognizable signs or symptoms in its earlier stages and can go undetected for years, preventive screenings to prevent illness and identify problems stand out as the missing link.
While most healthcare organizations purport to offer comprehensive public health and preventive medicine, only a percentage actually do. Because of this, innocent bystanders forego comprehensive health screenings, nutritional counseling, medication reviews, and educational activities that empower preventive self-advocacy.
Sadly, without this focus, chronic kidney disease patients inadvertently find themselves “sleep-walking” their way to dialysis without ever realizing they could have secured a better and longer life, given the chance.
Are practitioners to blame for this diagnosis dearth? Knowing patient education and screenings require additional time and resources (a commodity most healthcare providers lack), perhaps the insurance industry and healthcare system bureaucracy are target antagonists?
One might have thought that the passage of Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA), an incentive for physicians to offer more by participating in alternative payment models, would have solved this problem. Yet, chronic kidney disease specialists (nephrologists) can only participate in these models when caring for dialysis patients—something kidney patients hope to forestall or completely avoid.
Fortunately, newly proposed legislation now includes upfront payment models to improve early detection and diagnosis of kidney disease. The objective behind this admirable initiative is to provide physicians financial incentives to preventively screen, diagnose and educate their patients on how to slow the progression of their disease and secure their best treatment option.

The proposed model, known as H.R.3867, suggests a pilot program within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The model proposes a per-member-per-month payment structure, which would offer nephrologists a financial well that can be utilized to provide proactive patient engagement. This is particularly helpful for “change agent” practitioners who feel stuck because they don’t have the time or staff resources to provide this type of engagement.
In this new model, practitioners are encouraged to proactively engage their patients in shared decision-making for better outcomes. Moreover, early engagement offers an extended timeline to transplant candidates who are seeking a preemptive transplant (a transplant before the need for dialysis)—including additional time to help hopeful candidates find a living kidney donor.
Since this proposed payment structure already exists for dialysis patients, it should be a seamless act to expand on it. After all, shouldn’t the patient-centered goal be to reduce the incidence of people crashing into renal failure and requiring dialysis, rather than just managing dialysis? It could be the patient’s only chance to secure a better life.
Undeniably, early diagnosis, education, and engagement contribute to a chronic kidney disease patient’s quality of life. Early engagement can also reduce costs for insurance companies, lower hospitalizations and re-admissions, and decrease mortality rates; all of which are vital measuring sticks for dialysis and transplant centers.
It’s time to spread the word about this life-enhancing triple-win. Talk to your elected officials and make your voice heard.
Looking for patient engagement resources (books, seminars, webinars, mentoring and coaching) to empower patients to become their own best advocate, visit: www.TheProactivePath.com and www.ShiftYourFate.com. For programs on how to help transplant candidates end their wait by finding potential living kidney donors, visit: www.TransplantFirst.org
Article Snapshot: Proposed legislation to improve early diagnosis for chronic kidney disease and offer proactive patient engagement leads to better outcomes, by offering financial incentives to nephrologists.
Become A Living Kidney Donor-Magnet-Pro
Donor Magnet Pro’s are hopeful recipients and outreach teams who know how to enlighten listeners about what it takes to become a living kidney donor. This Top 12 FAQ List was recreated to help you share insights on what’s involved in living kidney donation.
- Who can be a living kidney donor?
Most people in good health can be evaluated to be considered as a living kidney donor. The qualification process typically begins with an online or telephone screening that determines if a thorough evaluation should follow. The evaluation typically includes several interviews, exams, scans and lab tests. The transplant center requires these tests to ensure the person who wishes to donate is healthy enough to do so.
- What does the process involve?
The Surgery:
The surgery is performed with small incisions, which is known as a laparoscopic surgery. In kidney donation (also known as a nephrectomy), the procedure typically involves four 1-inch slits in the area of the stomach and bladder. There is also one four-inch incision made around the navel. This incision is a bit larger, so the kidney can be removed from this area.
Risks:
The surgical process for removing a kidney from a healthy individual has become a fairly standard procedure. Nonetheless, the procedure still carries the same level of risk as any other major surgery. The most common risks associated with kidney donation (also known as a nephrectomy) includes blood clotting, infection and a reaction to the anesthesia. The risk of death from donating a kidney is less than one percent, or 0.0003 % (which is about 3 in every 10,000 surgeries).
Hospital Stay:
Hospital recovery usually involves 1-3 overnight stays. Discharge is determined by the donor’s health and their ability to get out of bed and walk on their own.
Discomfort:
Although the donor will feel pain after surgery, pain medications will be provided to help patient comfort. It is not uncommon for some patients to experience constipation from pain medication. When this is the case, laxatives are provided. FAQ: Understanding Living Kidney Donation.
Most living kidney donors can resume their regular activities within 3 weeks after donation. Depending on the type of work they perform, they can often go back to work within 3-5 weeks. If the donor’s work is office work, they can often get back to work even sooner. Those engaged in more strenuous activities are advised to refrain from these types of tasks until they are completely recovered.
- Who is going to pay for the cost of the procedure?
The medical insurance covering the individual who receives the donor’s kidney (and kidney transplant procedure) will also cover the donor’s medical costs. Things that are not covered or paid for (by the transplant patient’s insurance company) is the donor’s time off from work and travel costs. There are a few states that now require employers to cover living kidney donor’s time off work for a set period of time. *It is wise to check with employer policies, state laws and federal updates to ensure both donor and recipient are up-to-date.
- Can a donor still live a normal life after surgery?
There are many studies showing living kidney donors doing quite well after they donate a kidney. For the most part, their health and quality of life remains unchanged. The most notable change expressed by most living kidney donors comes in the form of the perpetual joy they feel for achieving such an extraordinary triumph.
Living kidney donors aren’t typically required to take new medications following the surgery, other than a pain medication or a stool softener for a short period of time. Kidney donors do not need to follow a special diet after they are discharged from the hospital. Likewise, they are not required to avoid alcohol, except for the period of time they would be taking pain medication. The guideline for alcohol consumption after kidney donation is fairly standard. Living kidney donors should be simply be responsible and consume alcohol in moderation.
- What emotions will the donor feel before or after surgery?
Like any excursion someone has never taken before, there can be a sense of excitement and anxiety about the journey ahead. Typically, the more one understands going into the process, the less anxiety they’ll experience. Post-surgery, most donors report a feeling of honor and joy from their heroic achievement. Remarkably, their sense of joy has reduced post-surgical pain and associated inconveniences.
- How successful are living kidney donor transplants?
Hospitals with established transplant programs show very good transplant success rates. Most transplant centers* exceed a 95% success rate one year after transplantation. The best success rates are seen in transplants from living kidney donors. (*Transplant programs are required to keep track of their success rates. Be sure to ask the center to share their success rates).
- Does the age of the donor matter?
Generally, there the ideal age range is 18-65 years old. Of course, the donor will need to prove (during their evaluation) that he or she is healthy enough to donate a kidney safely. While there have been donors who have donated a kidney after the age of 65; younger donors are preferred. Family members are also preferred, as they offer a better match. FAQ: Understanding Living Kidney Donation.
- What happens if the donor’s kidney isn’t a blood type match?
When the living kidney donor is not a match for their intended recipient (because they are incompatible in blood type or have antibodies to the recipient) they can still donate—just not directly. This is accomplished through a Paired Exchange Program.
In Paired Exchange, a computer algorithm is used to find a better match for incompatible groupings. In this model, the living kidney donor’s kidney is swapped with another person’s incompatible living kidney donor. The picture below illustrates this concept. In this scenario, a mother hoped to donate to a daughter and a brother hoped to donate to a sister. Both were unable to donate directly because it was determined that their kidneys would unlikely function well for their intended recipients. After they were told about the Paired Exchange Program, they agreed to be matched up with other incompatible pairs. In the example below, the mother donated to the brother’s sister, and the brother donated to the mother’s daughter. Though this example shows two incompatible pairs, it is not uncommon to see a larger grouping of individuals in a chained sequence of domino-like events.
- What happens if a donor changes their mind?
Interested donors can change their mind at any time about donating. Changes of this nature are kept confidential. The only information shared will be communicated as follows: “The donor was not an ideal candidate.”
- Will donating a kidney prevent the donor from getting pregnant or affect their sex life?
Donating a kidney has not shown to reduce the fertility of men or women. Because the body requires time to recover from the surgery of donating a kidney, it is recommended that women wait 3-6 months after donation to get pregnant. In the meantime, a donor can engage in sexual activities after their incisions have healed and they feel comfortable enough to do so.
- Does a kidney donor get anything for donating?
Legally, there can be no payment for kidney donation. Though, we are told that there is high value gained in the perpetual joy that comes with saving someone’s life. Some donors explain this as their highest “life achievement.” Others have called it their own “Mount Everest.” Living kidney donation is
a very personal experience. Not everyone can be a living kidney donor. It takes a very special person to connect to this humanitarian call. It also takes a very healthy person to even qualify.
- What’s the first step for someone to see if they’d qualify?
The first step is to call the kidney patient’s designated transplant center to schedule a telephone screening. During the call individuals can ask questions and get more details about the tests involved, the surgical procedure and recovery. Even if the person calling is not completely sure they want to proceed, this call can provide insight to help them decide if living kidney donation is right for them. All donor coordinator conversations are handled in strict confidence* to ensure callers can ask questions without pressure or concern. *The recipient will never know someone called in or their status, unless they tell them directly.
You Can Also Offer To Be a Back-Up
If someone has been told they are not needed (at this time), but they’re still interested in donating, they can offer to be a “backup.” This is important, should someone unexpectedly change their mind or be disqualified. (Often times, it takes several potential donors to be tested before a qualified match is found). If individuals are told they aren’t needed following the surgery, there is another way to proceed. They can also contact a hospital that performs kidney transplants in their area and tell them they’d like to be help one of their patients in need. An altruistic offer like this can often kick-off a Paired Exchange Chain. In these types of grouped events, one living kidney donor can offer extended life to a number of people in need. They do this by providing the missing link (their kidney) to be the final piece of the puzzle that completes the chain.
Key Benefits to Receiving a Transplant from a Living Donor:
- Ends the Wait
A kidney from a living donor “Ends the 3-9 Year Wait” for someone in need of a kidney transplant. The surgery can also be scheduled at the donor’s convenience when the kidney patient needs it most—and before their health declines, so they are not at risk for losing transplant eligibility.
- Offers a Better Match
Living kidney donors are thoroughly tested to ensure the best match for their recipients. Donor testing also minimizes potential risks for both the living kidney donor and the recipient.
- Offers Better Function
Kidneys from living donors are known to function immediately after transplant. They can also last twice as long as a kidney from a deceased donor. This could potentially equate into an additional 10-12 + years of function.
- Presents an Opportunity to Bypass Dialysis
Most kidney patients need to be on dialysis (to stay alive) while they wait for a deceased donor’s kidney. Hence, living kidney donors can help those in need receive a transplant before the need for dialysis. This is called a preemptive transplant. This process allows end-stage kidney disease patients to bypass* the need for dialysis altogether. *Note: Living kidney donors must be tested and approved for the surgery before the recipient’s function drops to a level of requiring dialysis.
For more information on how to become a Donor Magnet Pro, visit www.FindingKidneyDonors.com
Living Kidney Donation: What’s It Going To Cost?

Studies show that living donors may spend an average of $5,000 related to their donation — these include direct and indirect costs. A strong consensus exists to support a financially neutral impact to a live organ donor’s contribution to humanity.
To that end, the Live Donor Community of Practice of the American Society of Transplantation, along with the support of eleven other organizations, looked at systemic and financial barriers to living donation and developed a toolkit to give potential living donors financial resources to assist in making informed decisions about the donation process in advance of donation.
Areas that may financially impact living donors and care providers might include:
• The loss of wages associated with recovery time and testing procedures
• Transportation to the transplant center for testing, surgery and follow-up care
• Food, lodging, and incidentals for donation-related visits
• Paying for alternate caregiving plans – child care, elder care, pet care
• Forfeiting vacation time, holidays, sick days or FMLA for time off work
• Denials when purchasing disability or life insurance—or paying higher premiums.
• Job security concerns for employers who may not work absences associated with donation
• Uncovered medical expenses, which may vary by transplant center and by insurance contract. *(Potential donors should explore coverage of donor complications and follow-up).
This article contains considerable content excerpts from American Society of Transplant. See full details at this link: https://www.myast.org/sites/default/files/AST-16-Financial-Toolkit-Section-Intro.pdf
View sample cost-estimation worksheet pdf at MyAST link: https://www.myast.org/sites/default/files/AST-16-Financial-Toolkit-Section-1-Cost-Estimation-Worksheet.pdf
Financial Assistance Programs:
The National Living Donor Assistance Center (NLDAC) is a government funded program that provides financial assistance to eligible living donors for their travel expenses to the transplant center. Approved donors receive a special American Express controlled value card to pay for transportation, food, and lodging up to a total of $6,000. NLDAC will also pay for up to two trips for the donor’s support person(s). Eligibility is based on the recipient household yearly income, which should be no greater than 300% of the federal poverty guidelines (FPG). If the recipient household has an income greater than 300% of the FPG, a waiver for financial hardship may be requested. For complete 2016 information, see the NLDAC Brochure.
Learn more here: https://www.myast.org/sites/default/files/AST-16-Financial-Toolkit-Section-2-NLDAC-How-to-Apply.pdf
Proactive Patient Engagement Leads To Better Outcomes
New data reveals a lack of proactive patient engagement can lead kidney disease patients down a troubling path. While dialysis patients are promised more days of life, three of those days (every week) are spent tethered to a dialysis machine.
To make matters worse, the days in between treatments are filled with nausea, fatigue and lingering distress. Sadly, the decision to start dialysis often occurs in the 11th hour, with little if any proactive engagement. More often than not, end stage kidney disease patients have no idea what they’re getting into — or how they could have bypassed dialysis if they were transplant eligible and took a more proactive approach.
This is not a matter of accepting or rejecting dialysis. It’s a matter of fighting for the best life possible through proactive self-advocacy. It’s about slowing disease progression, managing symptoms and making lifestyle changes that preserve remaining kidney function. It’s about requesting an early evaluation and getting approved for a transplant before numbers get into the redzone (before GFR10). It’s about sharing one’s story and increasing awareness in our nation’s organ shortage and the need for more living kidney donors.
Did I get your attention? Is it time to become your own best advocate and secure a better future? Whether you’re hoping to avoid dialysis or get off dialysis by securing a living kidney donor transplant, learn how to use your voice and become a Donor Magnet Wizard today! Learn more here: www.findingkidneydonors.com
5 Ways To Help Someone With Kidney Disease
Did you know 31 million people in the US have kidney disease? Do you happen to know one of them? Wish you could help? You’re in luck—here’s 5 ways you can!
1. Keep Hydrated!
Hydration keeps kidneys strong and helps prevent kidney stones. Ensure your friends and family members with kidney disease are staying hydrated—and don’t forget to stay hydrated, as well. If they see you with a bottle, they’ll be more likely to grab one too!
2. Avoid Pain Relievers
Find ways to help someone with kidney disease relieve pain without the use of pain relieving products that are hard on your kidneys, like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin and Nurofen), aspirin and acetaminophen. Look for neutral ways to manage pain with doctor recommended stretching, meditation and Epsom salt baths.
3. Improve Habits
Eating less protein and more vegetable along with doctor-recommended exercise are great ways to care for your body and kidneys! If they’re cigarette smokers, encourage them to put those cigarettes down!
Smoking slows the blood flow to the kidneys and can make kidney disease worse.
4. Empower Engagement
Encourage kidney disease patients to learn as much as they can about slowing the progression of their disease. Information is power. Get them engaged with their doctors by helping them prepare a list of questions before they arrive to their appointments and don’t let them leave the office until their questions have been answered satisfactorily. Are care providers teaching them how to secure their best possible outcome? Empower kidney disease patients to use their voice and become their own best advocate. Learn more here: www.shiftyourfate.com
5. Improve Outcomes
Most kidney patients don’t realize they can avoid dialysis (or end their need for dialysis) by receiving a transplant from a living kidney donor. Currently, there are 100,000 people waiting for a kidney from a deceased organ donor, with an average wait of 5 years. Living kidney donors can end the wait.
This year, less than 18,000 people of the 100,000 waiting will receive a kidney transplant. Considering these statistics, your help is needed to increase awareness and interest in living kidney donation. Get involved today.
Learn more about living kidney donation here:
Learn how to find a living kidney donor here: www.findingkidneydonors.com.
Want to learn more?
Check out these powerful books on Amazon:
Shift Your Fate: Life-Changing Wisdom for Proactive Kidney Patients
Book page: www.shiftyourfate.com
In Pursuit of A Better Life: The Ultimate Guide For Finding Living Kidney Donors Book Page: www.findingkidneydonors.com